Traditional Woodworking Hand Tool Used to Remove Shavings

Woodworking is an age-vintage craft that combines artistry and talent to create useful and decorative gadgets from wooden. At the heart of this craft are the gear that allow woodworkers to shape and finish their tasks. One such vital tool, revered for its precision and versatility, is the hand aircraft. This traditional woodworking hand tool has been used for hundreds of years to do away with shavings, smooth surfaces, and create particular joints. In this text, we are able to discover the history, sorts, and uses of the hand aircraft, in conjunction with suggestions for selecting and maintaining this essential device.
History of the Hand Plane
The hand plane has a rich history that dates back to historic instances. Evidence of early hand planes has been observed in Egyptian tombs, wherein they were used to construct timber systems and fixtures. These early equipment were simple, generally such as a timber frame with an iron blade. Over the centuries, hand planes advanced in design and materials, with massive improvements at some point of the Roman Empire and the Middle Ages. By the 18th century, the contemporary hand plane commenced to take shape, incorporating capabilities like adjustable blades and improved ergonomics.
Types of Hand Planes
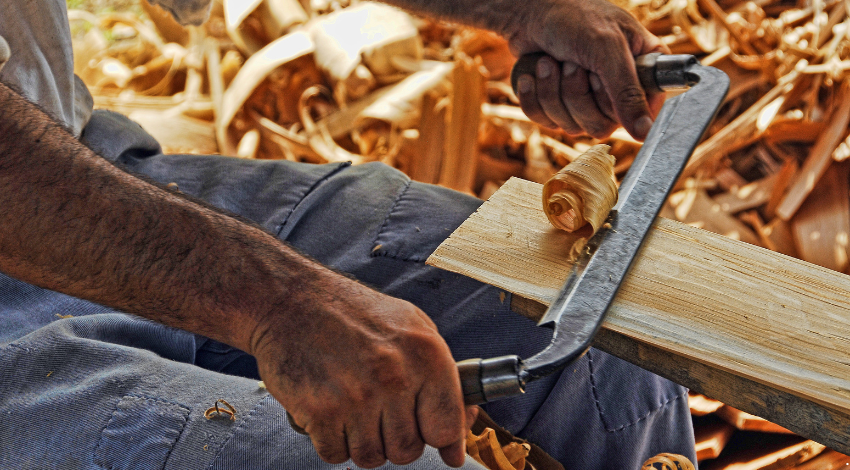

Hand planes come in diverse types, every designed for unique responsibilities in woodworking. Here are a number of the most common kinds:
1. Bench Planes
Bench planes are the workhorses of woodworking and are used for general smoothing and shaping tasks. They are available specific sizes, which include the jack aircraft, smoothing plane, and jointer plane. The jack plane is flexible and may cope with rough and satisfactory paintings, even as the smoothing plane is good for developing a clean end. The jointer aircraft is longer and used for flattening big surfaces and edges.
2. Block Planes
Block planes are smaller and extra compact than bench planes, making them best for trimming and pleasant-tuning paintings. They are normally used for stop grain paintings and small-scale projects. The low-perspective block plane is specially effective for cutting quit grain and working with hard wood grains.
three. Specialty Planes
Specialty planes are designed for specific obligations and encompass lots of precise designs. Examples include the rabbet aircraft, that is used for slicing rabbets and grooves, and the router aircraft, which is used for cleaning out and leveling recesses. Shoulder planes are designed for trimming tenons and different joints, even as molding planes create decorative profiles on wood edges.
Using a Hand Plane
Using a hand aircraft calls for ability and exercise, but with the right approach, it is able to produce top notch outcomes. Here are a few primary steps for using a hand aircraft:
1. Blade Adjustment
The first step is to modify the blade intensity and alignment. The blade must be set to protrude barely underneath the only of the plane. The intensity of cut may be adjusted based on the form of work being achieved.
2. Planing Technique
Hold the aircraft with each palms, with one hand at the the front knob and the other at the cope with. Apply even stress and push the plane forward along the wood grain. Keep the plane stage and use smooth, continuous strokes. For best outcomes, take mild shavings and keep away from eliminating an excessive amount of material at once.
three. Edge Planing
When planing edges, use a shooting board to manual the aircraft and ensure a immediately cut. This method is important for creating correct joints and clean edges.
4. Surface Planing
For large surfaces, use overlapping strokes to cowl the whole location. Check the surface regularly for flatness and regulate the blade as needed to reap the preferred finish.
Selecting and Maintaining a Hand Plane
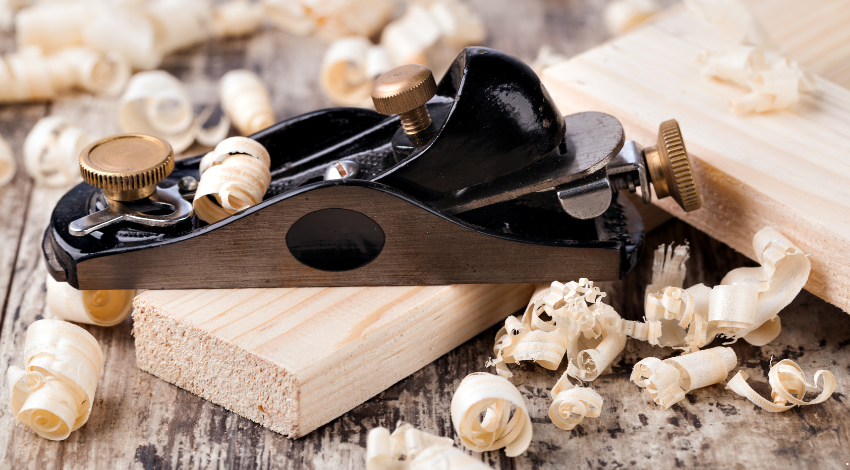

Choosing the proper hand aircraft includes considering factors just like the form of paintings, the first-class of the tool, and personal preference. Here are a few pointers for selecting and retaining a hand plane:
1. Quality and Material
Invest in a notable hand aircraft made from durable substances. Look for planes with well-machined additives and a comfortable grip. High-carbon metal blades maintain an area longer and provide better performance.
2. Blade Sharpening
Keep the blade sharp to ensure easy cuts and green planing. Use polishing stones or a honing guide to hold a sharp area. Regularly test and alter the blade alignment to maintain it in foremost situation.
3. Tool Care
Clean the aircraft after every use to remove dust and particles. Apply a mild coat of oil to the steel parts to prevent rust. Store the plane in a dry location to protect it from moisture and damage.
Conclusion
The hand aircraft is a undying tool that embodies the craftsmanship and precision of traditional woodworking. Whether you’re a seasoned woodworker or a newbie, getting to know the usage of a hand plane can increase your woodworking initiatives to new heights. By know-how the extraordinary styles of hand planes, learning the right techniques, and retaining your device, you can acquire easy, accurate, and exquisite outcomes for your woodworking endeavors. Embrace the artwork of hand planing and revel in the pride of working with this indispensable device.